Let's talk a bit about storage in GCP.
Hard disks for VMs is persistent and is block storage. In GCP we call is persistent storage. (block storage)
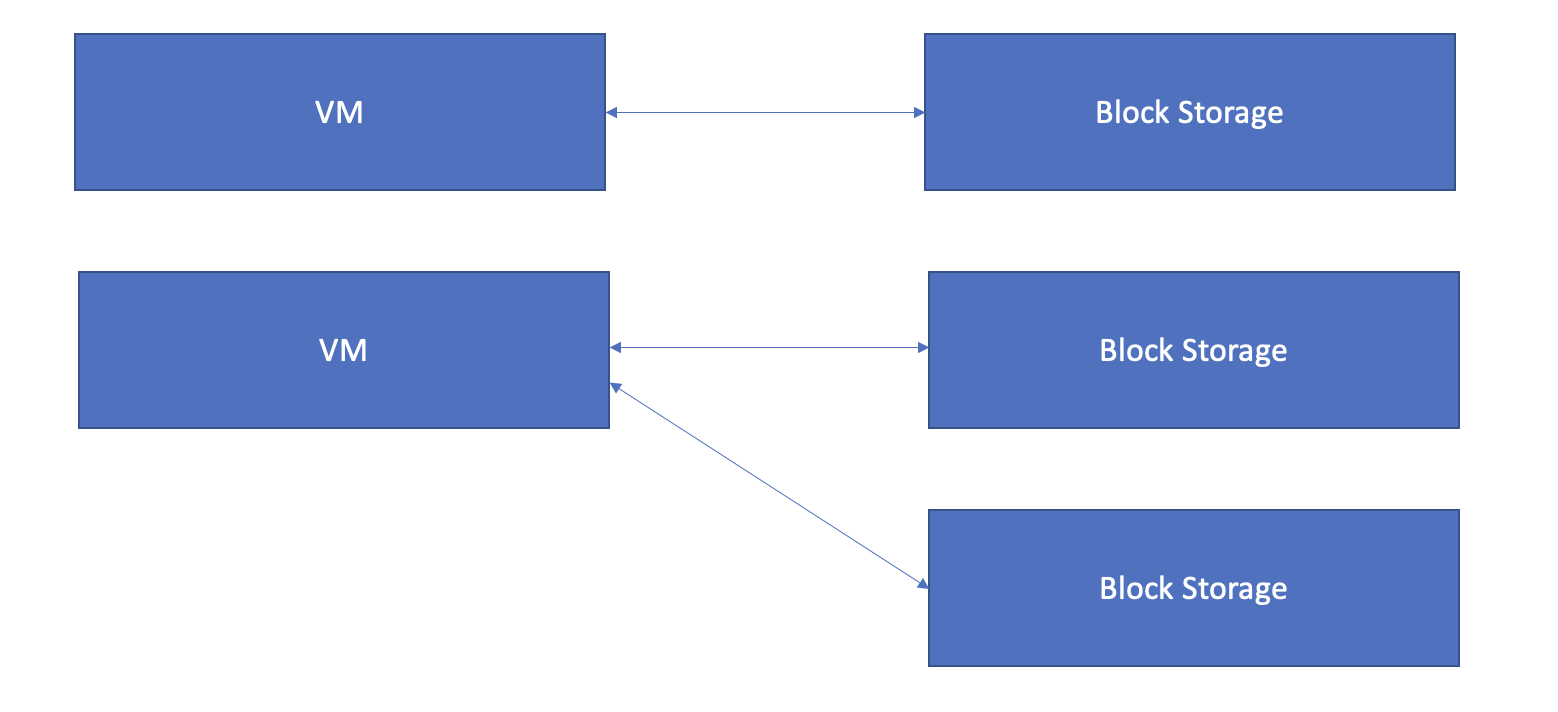
- As mentioned, this is similar to a hard drive of a computer.
- Only one block storage per VM. A block storage will map to one VM
- However, one VM can have different block storages.
- To avoid confusion on the above statements, look at the picture below
- Direct Attached storage is like a hard disk and Storage Area Network is like a pool of storage devices connected via a high speed network.
- GCP provides two options
- Persistent Disks
- Connected to a block storage via high speed network.
- Zonal - Data replicated in one zone
- Regional - Data replicated in multiple zones
- Logical to use Regional option for durability.
- By default a 10GB boot disk (persistent) is attached to a VM when we create a VM.
- Local SSDs
- Local block storage.
- Faster
- High performance
File store is for file storage and sharing between multiple VMs.
- Pretty logical, use file storages to store and share files across VMs.
Cloud storage in GCP is the object storage.
- Create a container (bucket in GCP) to store objects (use console)
- Bucket name has to be unique (globally)
- Location type
- Region (low latency)
- Dual region (2 regions) [High availability and low latency across 2 regions]
- Multi region (multiple regions) [High availability]
- Storage class
- Standard
- Short term
- Frequently accessed
- Near line
- Backups
- Data accessed less than one time a month
- Min storage duration is 1 month (30 days)
- Cold line
- Disaster recovery
- Data accessed less than once a quarter
- Min storage duration is 90 days
- Archive
- Long term data preservation (backup)
- Data accessed less than once a year
- Min storage duration is 365 days.
- Inexpensive
- Auto scales (as you add storage)
- Stored as key-value pair
- Access control at object level
- REST API available to access and modify stored objects
- Command line also available (gsutil command)
- Now logically one can store any type of data in the object storage.
- But some of these can be less frequently accessed (e.g backup files)
- Object storage helps to optimize costs based on access needs.
I have data on premise. How do I transfer to Google cloud?
Options:
- Online transfer:
- Transfer to Google cloud storage via APIs or CLI (gsutil) [< 1TB]
- Good for smaller sized transfer (not for peta byte sized data)
- Storage Transfer:
- Peta byte sized data
- Setup a recurring repeating schedule
- Can be an incremental transfer as well.
- Fault tolerant - starts from where it failed.
- Use when
- > 1TB of data
- Transferring from different cloud
- Transfer Appliance is physical data transfer.
- Size > 20TB
- Request an appliance.
- Upload data to the appliance (e.g USB type appliance)
- Ship the appliance
- Google uploads to storage.
- Data is encrypted in the appliance
- Two appliance devices
- TA40 (for upto 40 TB)
- TA300 (for upto 300 TB)

No comments:
Post a Comment