Multiple Linear Regression is a regression model where we have multiple independent variables.
We need to predict values for the dependent variable as a function of the independent variables.
Formula for Multiple Linear Regression:
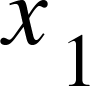 onwards are the the independent Variable
onwards are the the independent Variable
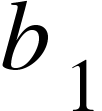 onwards is the coefficient (connector between dependent and Independent)
onwards is the coefficient (connector between dependent and Independent)
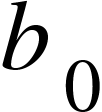 is the Constant
is the Constant
Always encode the categorical data if any after data import.
We need to predict values for the dependent variable as a function of the independent variables.
Formula for Multiple Linear Regression:
where
y is the dependent Variable
Always encode the categorical data if any after data import.
Code Snippet:
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
multi_regressor = LinearRegression()
multi_regressor.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Prediction
y_pred = multi_regressor.predict(X_test)




